One of the most common sleep disorders out there is sleep apnea. But what does it actually do to your health? Learn about sleep apnea and how it can be treated.
Sleep apnea is when a person experiences pauses in breathing during sleep. This can be noticed by bed partners or family members who might have seen the patient during sleep.
It can be dangerous since it can interrupt a person’s breathing for seconds that may last up to minutes. This will eventually affect the heart and brain and may cause other illnesses.
Diagnosis
Sleep apnea is most commonly diagnosed through the help of a sleep study (polysomnography).
- Polysomnography (Sleep Study)
- The overall method to diagnose sleep-related conditions is called a “polysomnography” or a sleep study / sleep test, it uses all possible methods to diagnose a person’s condition
- Actigraphy
- Actigraphy is similar to polysomnography but less expensive. It is used to record the sleep and wake cycles, by analyzing the patient’s limb movements.
It is also helpful in ruling out other sleep disorders, especially circadian disorders, leading to an excess of sleepiness during the day, too.
(Related: “How to Do a Sleep Study?”)
- Actigraphy is similar to polysomnography but less expensive. It is used to record the sleep and wake cycles, by analyzing the patient’s limb movements.
- Actigraphy
- The overall method to diagnose sleep-related conditions is called a “polysomnography” or a sleep study / sleep test, it uses all possible methods to diagnose a person’s condition
You will be asked several questions at first like an initial interview (assessment criteria) to see if you need to get diagnosed.
Questions you can expect when you are scheduling your sleep study appointment are the following:
- Do you snore constantly and loudly?
- Do you experience pauses in breathing during sleep?
- Are you a heavy drinker?
- Do you exercise frequently?
- Do you smoke a lot?
- Does your family have a history of sleep apnea?
- Do you feel tired right after waking up?
Signs of sleep apnea can be observed by bed partners or family members who are close to the patient.
Diagnosing sleep apnea can be easy with the help of a sleep diary.
A sleep diary keeps track of time to bed, total sleep time, time to sleep onset, number of awakenings, use of medications, time of awakening, and subjective feelings in the morning.
Sleep apnea is measured by a unit referred to as “Apnea-Hypopnea Index” or shortly called “AHI” and this is used during a sleep study session.
The Apnea-Hypopnea Index is an index used to indicate the severity of sleep apnea and it is represented by the number of apnea and hypopnea events per hour of sleep.
For example, a good AHI score or Apnea-Hypopnea Index should be at “<5” which is a normal rate. For mild, it’s 5<15 and for moderate sleep apnea, 15<30. For severe sleep apnea, it’s beyond 15<30.
So, depending on how many times you experience an “apnea” event or a “hypopnea” event, your AHI score or “sleep apnea score” may also be different.
The more apnea events that occur during your sleep, the higher your AHI score will be and the more it is likely that you do have sleep apnea.
(Related: “How is Sleep Apnea Measured?“)
Types of Sleep Apnea
There are three types of sleep apnea. Sleep apnea can come independently or come as a sign of another existing disease.
For some cases, sleep apnea may go away on its own but most of the time, sleep apnea requires medical attention for proper treatment.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea is the most common type of sleep apnea that can be present in all ages.
It occurs when the breathing is obstructed. For example, the upper airways (the throat) is blocked by certain factors.
Obstructive sleep apnea may require surgery for treatment unlike other types of sleep apnea that can go away on its own.
Central Sleep Apnea
When your brain fails to send the proper signals to your body to command it to “breathe”, it is because of central sleep apnea
This conditions “attacks” when the brain is unable to send proper signals to our muscles that control breathing. In other words, you may think of it as a dysfunctional machine unable to work properly.
Unlike the common obstructive sleep apnea which disrupts breathing due to an obstruction in the upper airway, central sleep apnea happens simply because of the affected brain, not the airways itself.
Central sleep apnea is less common than obstructive sleep apnea. Central sleep apnea may occur as a result of other conditions, such as heart failure and stroke.
Sleeping at a high altitude also may cause central sleep apnea.
Treatments for central sleep apnea may involve treating existing conditions, using a device to assist breathing or using supplemental oxygen.
(Related: “How to Reverse Central Sleep Apnea“)
Complex Sleep Apnea
Complex sleep apnea is the combination of the first two sleep apneas (Obstructive sleep apnea and central sleep apnea) and also poses higher risks than a normal obstructed sleep apnea.
It may also be more difficult to treat this not knowing the major cause of the condition.
Causes
There are different potential causes behind sleep apnea. The factors listed can be applicable for each type of sleep apnea. Complex sleep apnea is a combination of both types of sleep apnea.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
- Being overweight
- Body fat can get in the way of the body’s ability to stretch its airways open making it harder to breathe which will cause sleep apnea.
- Airway obstruction
- Anything that can obstruct the airways will make breathing difficult and cause the tissues to vibrate and cause sleep apnea.
- Sleeping position
- Sleeping on your back may cause the tongue to fall back and the muscles to relax which can block the airways.
- Drinking liquor
- Drinking excessive liquor especially before going to sleep will relax the muscles and create difficulty in breathing.
- Taking medications
- Certain medications can make the body relax as well
- Sleeping exhausted
- Sometimes, going to bed overworked or completely exhausted can cause sleep apnea since the body is too tired to help your breathing stay normal.
- Anatomical build
- Your physical attributes can obstruct your airways and some of this can be hereditary.
- Age
- As we age, our throat will become narrower which is beyond our control. However, proper sleep routine and a healthy, balanced diet can prevent snoring or sleep apnea.
- Hypothyroidism
- The condition wherein your body does not produce enough thyroid hormones, which is needed to control how to use energy received from food through metabolism. Bad metabolism can affect heartbeat and breathing.
- Acromegaly
- Opposite of hypothyroidism, acromegaly produces too much growth hormones which can affect your overall health including breathing.
- Allergies
- There are certain allergies that can worsen sleep apnea or snoring. Allergies that result with difficulty in breathing are the likes.
- Smoking cigarettes
- Excessive smoking can cause your throat muscles to swell, making the airways narrower and lead to obstruction, causing sleep apnea.
- Sleeping with a full stomach
- When you go to bed with a full stomach, there’s a risk of relaxing your muscles or your body is working on processing the food inside your body which can lead to difficult breathing.
- Going to bed exhausted
- Try to take a quick break before going to bed. If you are too tired and went to sleep, your muscles won’t work as it should and may not keep you breathing right during sleep.
- Lack of physical activity
- The lack of physical activity can weaken your muscles, making it unable to sustain your body’s need to keep breathing during sleep.
Central Sleep Apnea (CSA)
- Cheyne-Stokes breathing
- This type of central sleep apnea is most commonly associated with congestive heart failure or stroke. Cheyne-Stokes breathing involves irregular breathing patterns.
- Drug-induced apnea
- Taking certain medications such as opioids may cause your breathing to become irregular, to increase and decrease in a regular pattern, or to temporarily stop completely.
- High-altitude periodic breathing
- A Cheyne-Stokes breathing pattern may occur if you’re exposed to a very high altitude.
- The change in oxygen at this altitude is the reason for the alternating rapid breathing (hyperventilation) and under breathing.
- CPAP treatment induced
- Some people with obstructive sleep apnea develop central sleep apnea while using continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) for their sleep apnea treatment.
- This condition is known as treatment-emergent central sleep apnea and is a combination of obstructive and central sleep apneas.
- Medical condition-induced CSA
- Several medical conditions, including end-stage kidney disease and stroke, may give rise to central sleep apnea of the non-Cheyne-Stokes variety.
- Idiopathic (primary) central sleep apnea
- The cause of this uncommon type of central sleep apnea is still currently being studied. As of the moment, the cause is unknown.
Risk Factors
There are also certain factors that may worsen sleep apnea or may put a person in a lot more risk of getting diagnosed with sleep apnea.
- Obesity
- Can make breathing difficult even while asleep or not moving
- Hypothyroidism
- The condition wherein your body does not produce enough thyroid hormones, which is needed to control how to use energy received from food through metabolism. Bad metabolism can affect heartbeat and breathing.
- Acromegaly
- Opposite of hypothyroidism, acromegaly produces too much growth hormones which can affect your overall health including breathing.
- Allergies
- There are certain allergies that can worsen sleep apnea. Allergies that result with difficulty in breathing are the likes.
- Smoking cigarettes
- Excessive smoking can damage your body which may make it harder to function or relax properly, increasing the risk of sleep apnea
- Drinking liquor
- Too much liquor and drinking before going to sleep can cause sleep apnea.
- Drug usage
- Sedations or other types of drugs especially when being abused can result in sleep apnea or worse.
- Certain drugs, medications or such can worsen sleep apnea and lead to sudden death
- Being male
- Observations reveal that males tend to have sleep apnea more than females
- Though this factor cannot be avoided, knowing about it will help you understand the reason why you are prone to sleep apnea
- Being old
- Observations also revealed that older adults are more prone to sleep apnea than younger ones due to more complicated health issues that may trigger sleep apnea
Other natural causes of obstructive sleep apnea can be a thick neck, narrow throat and having a round head. Avoid triggering your allergies or get medications for other conditions to cure your sleep apnea.
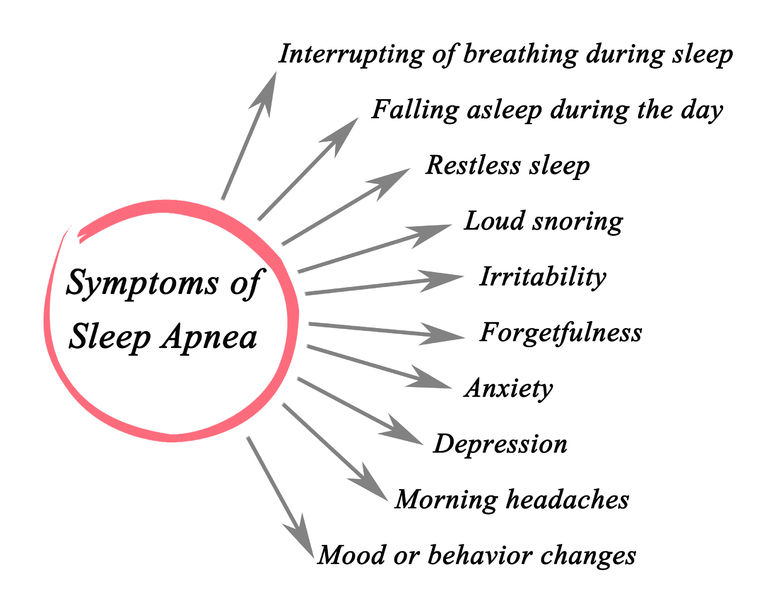
Symptoms
The main symptom of sleep apnea is experiencing sudden pauses in breathing during sleep. It may cause a person to wake up in the middle of the night, but the person may not even notice it sometimes.
- Heavy snoring
- Maybe, it can be a sign of fatigue but snoring loudly and usually can be a sign of sleep apnea.
- Gasping for air during sleep
- The feeling of drowning without knowing it and suddenly you’re out of air.
- Insomnia
- Having trouble going to sleep because you have breathing problems that you may not notice
- This is also why we feel sick later on, the lack of sleep means lack of energy.
- Hypersomnia
- Having trouble staying awake in the morning because you were unable to sleep well due to your obstructive sleep apnea. We may also confuse sleepiness for sickness.
- Sudden weight gain or loss
- Obstructive sleep apnea can lead to uncontrolled weight gain or weight loss for some cases. It’s because of the uncontrollable hormones affected by sleep deprivation.
- Waking up with a headache
- Obstructive sleep apnea can disturb your body’s “charging” state. Since you can’t sleep well, your body will use energy for means that can help you breathe which may lead to headaches.
- Waking up with a dry mouth
- With obstructive sleep apnea, the person tends to snore and keep their mouth open when gasping for air which leads to a dried up mouth once we awaken.
- Decreased ability to focus
- Obstructive sleep apnea can give lack of sleep which will also result in difficulty to focus on anything
- Feeling uncomfortable
- Your lack of energy due to obstructive sleep apnea can make you feel uncomfortable and irritable without your knowledge
- Suddenly stop breathing during sleep
- Your housemates should notice this and tell you about it. Obstructive sleep apnea can disrupt breathing that may last for up to 10 seconds which is already risky.
Treatment
Treatment for sleep apnea will be different depending on what causes it in the first place. Diagnosing which type of sleep apnea a person might have is important to determine the best treatment options.
If a person is diagnosed with central sleep apnea, any of the following treatments may work well for them. If sleep apnea appears as a sign of another disease, the existing disease must be the main focus of treatment.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
- Rapid Maxillary Expansion
- For children with obstructive sleep apnea. This process places an expandable brace on the roof of the mouth that increases the width of the upper jaw (maxilla).
- Over time, parents can adjust the brace using a special key to increase the amount of pressure for the teeth.
- Jaw Advancement Surgery
- For teenagers and adults. This process will surgically break the jaw bones, moved forward and then fixed properly with screws and plates and will change the person’s facial structure or profile.
- It might take months to recover.
- Surgical Airway Advancement
- Similar to the 2nd example. Bones of the upper and lower jaw will be repositioned in a way that will relieve airway obstruction.
- Nasal Strips
- Nasal strips are one of the earliest tools used to treat conditions like sleep apnea and its symptoms such as snoring.
Nowadays, there are newly developed nasal strips that you can try.
- Nasal strips are one of the earliest tools used to treat conditions like sleep apnea and its symptoms such as snoring.
- Oral Appliance
- Oral pieces can help with sleep apnea and snoring, they are custom made to make sure it prevents the obstruction in the airways and counter sleep apnea and snoring.
- CPAP Treatment
- The CPAP or “Continuous Positive Airway Pressure” is a commonly used treatment and proven to be effective for sleep apnea patients and helping snoring.
- Avoid sedatives before going to sleep
- Certain sedatives can cause sleep apnea. Consult a medical expert to determine what type of sedative may be the cause.
- Treat chronic allergies
- Some allergies can trigger obstruction in your body’s airways and may cause you to have sleep apnea and cause you to snore.
- Try to avoid overworking yourself.
- Sometimes, simply going to sleep while totally exhausted can make our muscles relax too much to the point that it can lead to sleep apnea.
- Avoid drinking liquor before bed.
- Excessive liquor can also relax the muscles that will lead to sleep apnea. Limit alcohol consumption or avoid drinking too much before going to sleep.
- Sleep with your head elevated.
- When the head is not properly elevated, the tongue can fall back and block the air passage, causing the tissues to vibrate and snore.
You can also use an anti-snore pillow which will keep your head in proper place that can help stop sleep apnea. Sleeping in a chair or a recliner chair is also an option.
- When the head is not properly elevated, the tongue can fall back and block the air passage, causing the tissues to vibrate and snore.
- Try to sleep on your sides.
- Sleeping flat on our backs can cause the tongue to fall back and block the airways. It can also make the muscles relax and cause sleep apnea.
You can read about: “How to prevent sleeping on my back” to learn how you can keep sleeping on your sides.
- Sleeping flat on our backs can cause the tongue to fall back and block the airways. It can also make the muscles relax and cause sleep apnea.
- Get plenty of exercises.
- Lack of physical activity can cause our body’s functionality to drop. This means that we need the right amount of exercise to keep our body “awake” and functioning even as we sleep.
- Stop or limit smoking.
- If your body inhales the smoke, it can cause the muscles inside to swell or become irritated, potentially blocking the airways and causing you to snore.
Those who are also exposed to secondhand smoke can be prone to sleep apnea, so avoid getting near smoke as much as possible.
- If your body inhales the smoke, it can cause the muscles inside to swell or become irritated, potentially blocking the airways and causing you to snore.
- Drink enough water.
- When we are dehydrated, the throat becomes dry which makes the vibrating tissues sound louder and produces snoring or sleep apnea. Stay hydrated!
- Eat a healthy diet.
- Our diet plays a huge part in our health! You should also avoid eating heavy before sleeping, if you go to sleep on a full stomach, your muscles may not work as it should.
Focus on eating healthy foods!
- Our diet plays a huge part in our health! You should also avoid eating heavy before sleeping, if you go to sleep on a full stomach, your muscles may not work as it should.
- Sleep on time.
- Not getting the right amount of sleep and not sleeping early can cause the body to become dysfunctional and have sleep apnea.
- Lose weight.
- Being overweight or obesity will cause difficulty in breathing. The excess fat will get in the way of the air passages, causing tissues to vibrate and cause sleep apnea.
Central Sleep Apnea (CSA)
- CPAP treatment
- CPAP or “Continuous Positive Airway Pressure” is the most commonly used method for treating sleep apnea of all types. Providing the air you need, it can eventually cure sleep apnea.
- Treating associated conditions
- Central sleep apnea can be caused by different health conditions. For example, treating risks of heart failure can get rid of central sleep apnea.
- Reducing opioid medications
- If you are taking opioid medications, there’s a chance that it may be the cause of your central sleep apnea. Reducing the dosage can potentially reverse central sleep apnea.
- Bilevel positive airway pressure
- Bilevel positive airway pressure (BPAP) is similar to CPAP and ASV treatment methods but also have its own risks especially for patients with heart failure.
- Adaptive servo-ventilation
- Also similar to CPAP treatment, adaptive servo-ventilation provides positive air to its users and is capable of adjusting the pressure during use for better treatment of the patient.
- Supplemental oxygen
- Just like CPAP, using supplemental oxygen can help reverse central sleep apnea. Supplemental oxygen can be delivered to your lungs in various ways.
- Acetazolamide or Diamox medication
- Certain medications such as Acetazolamide can help treat central sleep apnea. There are also more, but you must consult your doctor for more accurate prescriptions.
- Phrenic nerve stimulation
- A surgery where a nerve stimulator device is implanted inside the body to help keep your body breathing during sleep. It only works when you are lying down.
There are also basic lifestyle changes that can help prevent central sleep apnea such as the following…
- Losing weight
- For some cases, being overweight can worsen central sleep apnea. This can lead to a combination of CSA and OSA which will result in complex sleep apnea.
- Avoiding alcohol
- Excessive liquor consumption can also worsen central sleep apnea, avoiding this can help you reverse the condition much easier.
- Avoiding smoking
- Smoking can also worsen sleep apnea so it’s best for you to try to limit your intake or if possible, permanently stop it.
- Avoiding sedative drugs
- Certain drugs can relax the muscles too much to the point that it will make breathing even more difficult, worsening central sleep apnea conditions.
- Sleeping on time
- Sometimes, we end up triggering sleep apnea simply because we do not sleep early or properly. Try to follow a proper sleeping routine and avoid central sleep apnea.
- Sleeping on your sides
- Sleeping on your sides can help reduce the tendency of sleep apnea attacks.
- Treating chronic allergies
- Allergic reactions that may involve difficulty in breathing can be the cause of sleep apnea or worsen it. Treating or avoiding your allergies can also prevent central sleep apnea.
- Using anti-apnea devices
- There are now a lot of anti-sleep apnea devices that can be tried depending on what your doctor prescribes.
Risks
Untreated sleep apnea is dangerous for the health especially in the long run. Regardless of the time, it carries a lot of health risks for a patient.
- Sleep apnea causes:
- Death
- Sleep apnea interrupts breathing that can affect the heart and the brain which can lead to sudden death during sleep.
- Difficult breathing
- Sleep apnea can occur when there is an obstruction in the airway or the brain is unable to function well that helps the body breathe, causing difficult breathing.
- Snoring
- If there is an obstruction in the airway, the muscles around the throat may vibrate and cause snoring.
- Worsens other illnesses
- Being unable to breathe well during sleep disrupts your entire body’s functionality and eventually attacking the other diseases a patient may already have.
- Heart problems
- With sleep apnea, you are more prone to heart problems such as heart failure or heart attacks. This is due to the lack of blood oxygen levels.
- Irregular heartbeat
- Due to the low blood oxygen levels or the air is unable to reach your heart, it can lead to an abnormal heartbeat or pauses in breathing during sleep.
- Stroke
- Similar to heart problems
- Depression
- Being unable to breathe well during sleep and get the proper rest can mess up your emotions or eventually lead to depression.
- Weight gain or loss
- Sleep apnea messes up your body’s hormone production. You can end up gaining weight faster due to sleep apnea.
- Diabetes
- Having sleep apnea disables the body’s ability to control the sugar level which can lead to diabetes.
- High Blood Pressure
- Sleep apnea can potentially cause or worsen hypertension in people.
- Increases ADHD
- Being sleep deprived decreases the person’s ability to focus, worsening conditions such as ADHD.
- Headaches
- The lack of air that enters the brain can lead to other brain problems, but usually results in morning headaches.
- Daytime sleepiness
- Difficulty breathing at night can lead to restless sleeps, making you feel the need to stay asleep even during the day because your body couldn’t rest well at night.
- Insomnia
- Difficulty in breathing can lead to insomnia. Instead of waking up randomly at night, you will end up being unable to sleep.
- Seizures
- Sleep apnea patients are more prone to seizures during sleep compared to epilepsy patients without sleep apnea.
- Irritability
- When you are sleep deprived, you will unconsciously lose control of your emotional stability. You can become irritable or easily frustrated with sleep apnea.
- Poor memory
- Sleep apnea causes sleep deprivation which may lower your brain’s performance as it affects the brain activity, causing poor memory in patients.
- Respiratory diseases
- Sleep apnea is a respiratory disease that may cause other diseases or worsen them.
- Driving accidents
- The lack of concentration and daytime sleepiness can lead to driving accidents when you have sleep apnea.
- Death
Related Questions
Can Sleep Apnea kill you?
Yes, untreated sleep apnea can end up becoming the cause of one’s death. There are already reported cases of deaths with sleep apnea patients.
Sleep apnea is already deadly with its symptoms of disrupting breathing and heartbeat during sleep but it also invites other threatening illnesses which means, if untreated, it can easily turn fatal any moment.
Does sleep apnea happen every night?
Yes, sleep apnea usually happens every night for most patients. Breathing usually stops for a few seconds up to minutes during sleep which is very dangerous.
The pauses in breathing can occur up to 400 times each night.
However, those whose sleep apnea is “temporary” or not a chronic illness may avoid experiencing sleep apnea every night. Sometimes, it can also depend on the severity of the illness.