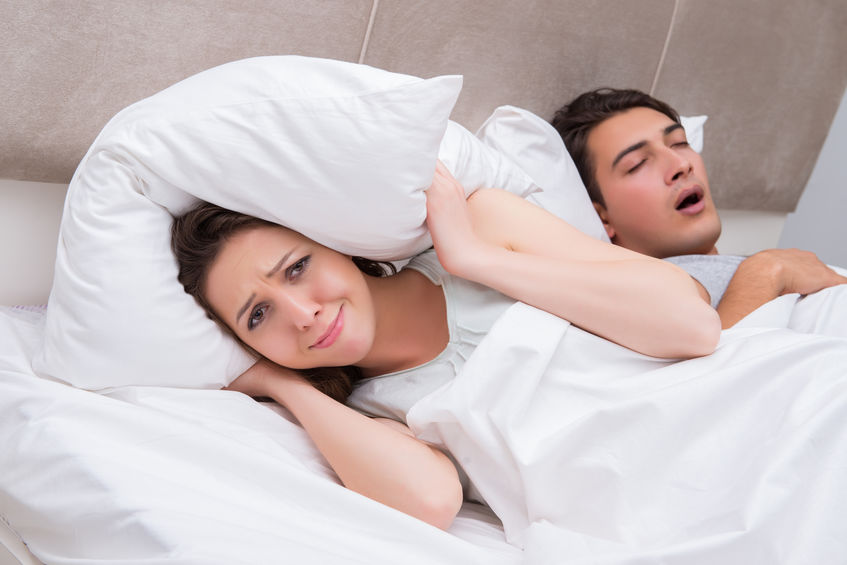
Snoring is one of the biggest sleeping problems that lead to even bigger health problems, so it’s important to find out as much as you can about it if you want to stop the habit.
When does snoring occur? Snoring occurs when the air is unable to freely pass through your airways while you sleep. It can be caused by different obstructions around your throat or nasal areas. The sound comes from the air trying to force its way through your airways.
As you read further, you’ll better understand what causes people to snore. You’ll also learn about its symptoms and effects, and find out how to stop snoring.
Why Do People Snore?
When you sleep, every part of your body starts to relax. As you fall into an even deeper sleep, your body relaxes even further. This causes the tissues and muscles around your soft palate, tongue and throat to collapse into your airways.
When this happens, they form an obstruction that makes it harder for air to pass through. The tissues then vibrate as the air forces its way through, which results to the snoring sound you hear.
There are a number of factors that contribute to this occurrence even further. Here are some of the most common:
- Age. As we get older, our throat becomes narrower. Our muscle tone also decreases, which means that it is easier for the tissue around our throat to sag. This makes them collapse further down the already narrow throat, causing an obstruction.
- Alcohol and medications. Alcohol, as well as a few other medications, cause your body to over-relax when you sleep. This means that your throat tissues and muscles sag even more while you sleep.
- Excess weight. When you are overweight, you’ll find that there are a lot of fat deposits that gather around your neck. This makes your airways narrower.
- Anatomy. Some people are just naturally born with narrow airways. Some traits are also hereditary, like having large adenoids or having a cleft palate. Men are also, by nature, more likely to snore than women because their throats are narrower.
- Nasal and sinus congestion. Air does not just pass through your throat, it passes through your nasal passages as well. So if there is any form of congestion in your nasal passages, this will still contribute to your snoring.
- Smoking. Smoking causes inflammation in the airways and nasal passages. This contributes to the narrowing of the airways.
- Sleeping position. When you sleep on your back, you are letting your loose muscles and tissues just collapse back into your throat. You may also restrict your breathing if your neck is angled the wrong way, especially if your pillow is too high.
Seeing the different contributors to your snoring, it’s easy to see that a few lifestyle changes may also be in order if you want to stop it from happening.
What are the Symptoms of Snoring?
If you do not have a roommate, it may be tough to tell if you snore at night or not. The good news is, you can watch out for symptoms that may tell you that you might be snoring at night without you knowing.
Here are those symptoms:
- Restless sleep
- Excessive drowsiness during the day
- Morning headaches
- Dryness or soreness of throat upon waking up
- Lack of focus during the day
- Chest pains, especially at night
- Irritability and mood swings
- Forgetfulness
Basically, these symptoms of snoring show that you are unable to get enough quality sleep at night, which, in turn, affects your behavior and overall well-being during the day.
What are the Health Risks of Snoring?
Snoring is often dismissed as a simple sleeping disorder, but it’s actually more serious than that. Snoring can lead to a number of health risks that may affect the quality and length of your life.
Here are some of those health risks:
- Stroke. The worse your snoring gets, the higher the chances of you getting a stroke as well. Studies show that the intensity of your snoring is related to the narrowing of the arteries on your neck. This happens because of the buildup of fats, tissue, calcium and other debris.
- Heart disease. People who snore would often stop breathing for a few seconds to a few minutes. The brain would then jolt the snorer awake with a blast of hormones, prompting the heart to work double time in pumping more blood throughout the body. With the heart going through this kind of stress a few times each night, it’s not surprising that it’s also one of the first organs to break down for regular snorers.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease. GERD is a condition where the contents of the stomach rises back up to the esophagus. This is one of the reasons why some people suffer from acid indigestion and heartburn. The irregularity on how your throat opens and closes causes pressure from the throat to the stomach, resulting to GERD.
- Accidents and injuries. People who snore do not enjoy quality sleep. Because of the frequent sleep interruptions, you end up drowsy and lacking focus in the daytime. This is why snorers are more prone to accidents and injuries.
- Mental health issues. The lack of focus, forgetfulness, and irritability during the day can make snorers unproductive. Their relationships could also suffer. This is why a lot of snorers may eventually develop anxiety or depression.
Other health risks include arrhythmia, headaches, obesity, and more. As you can probably tell by now, snoring cannot be take lightly.
How Can You Stop Snoring?
Now that we know how serious smoking really is, it’s time to found out what you can do to stop it.
- Lose some weight. Losing weight can help you widen up your airways, especially if a lot of the fat deposits are settling around your neck. This makes it easier for you to breathe, especially when sleeping.
- Sleep on your side. Remember how we discussed that sleeping on your back will only make your throat and tongue muscles collapse further into your throat, causing an obstruction in your airways? Sleeping on your side is the best solution for this. Support your body will pillows so that you don’t fall on your back when you’re deep into your sleep.
- Treat your allergies. Allergies is one of the most common sources of congestion. Allergens like dust, molds, air toxins and the like can cause your throat and nasal passages to swell. So make sure you clean your bedroom regularly, change the sheets often, and get rid of old pillows that could be housing dust mites. Always check air ducts and fix any water damage right away.
- Set a healthy routine before bed. Make sure you avoid heavy meals at least 3 to 4 hours before going to bed. Avoid drinking alcohol within that same time frame as well. Steer clear of sedatives that could over-relax you.
- Get enough rest. Don’t tire yourself out too much so that you can avoid collapsing into bed at the end of the day. Try to get 8 hours of sleep as well so that you can have enough energy for the next day, helping you prevent overfatigue.
- Use a CPAP. A CPAP or continuous positive airway pressure is a machine that consistently pumps air pressure into your airways while you sleep. You would have to wear a mask while sleeping, which can prove to be uncomfortable at first. But it’s the best way to stop smoking, especially if you have obstructive sleep apnea.
- Ask a sleep specialist for treatment recommendations. A sleep specialist and your doctor would be able to tell you if further treatments are required. In some cases, you may also be asked to go through surgery, or to use other kinds of oral appliances.
Getting rid of your snoring will not be an automatic thing. For some, it may require a lot of hard work. But if it means avoiding the health risks that snoring can lead to, then it’s all going to be worth it.
Related Questions
Is snoring a sign of deep sleep?
Snoring does not always mean deep sleep. For those who have congested nasal passages, obstructed airways, and sleep apnea, you could start snoring even if your only sleeping lightly.
How do you sleep with someone who snores?
You can try going to bed before the snorer falls asleep. A pair of ear plugs would be a good investment as well. Some people who have snoring roommates also say that some white noise helps them sleep better despite the snoring.